| Neural Network Toolbox | Search Help Desk |
| logsig | Examples See Also |
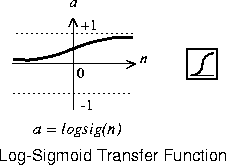
A = logsig(N)
info = logsig(code)
logsig is a transfer function. Transfer functions calculate a layer's output from its net input.
logsig(N) takes one input,
N - S x Q matrix of net input (column) vectors.
N squashed between 0 and 1.
logsig(code) returns useful information for each code string:
Here is the code to create a plot of the logsig transfer function.
n = -5:0.1:5; a = logsig(n); plot(n,a)You can create a standard network that uses
logsig by calling newff or newcf.
To change a network so a layer uses logsig set net.layers{i}.transferFcn to 'logsig'.
In either case, call sim to simulate the network with purelin.
See newff or newcf for simulation examples.
logsig(n) = 1 / (1 + exp(-n))
sim,dlogsig,tansig