 |
CS 150 Computer Literacy Programming |
 |
A computer program (computer application)is a set of instructions
that directs a computer to perform tasks.
A computer programmer creates the instructions using a programming
language.
A programming language is a set of words, symbols, and codes that
enables a programmer to communicate instructions to a computer.
Creating a program
1. First you design the program, sometimes called pseudocode. Pseudcode is writing out the program in plain English so it is easily understood and the flow can be easily tracked.
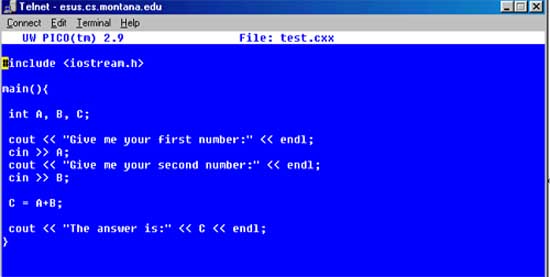
2. Write the Source Code. Source Code is the program written in the proper syntax for a particular programming language.
- The following is source code written in C++ programming language.
Next this source code must be put through a Compiler which changes the source code into machine language that the computer (processor) can understand. Machine language is the executable file that users such as yourself run, like as in Word or Excel. Machine language cannot be understood by reading it as a text file.
An explanation of the code above:
- The first line is ..#include <iostream.h> .. is a library call that allows the programmer to make system calls so it can print to the screen and receive input from the keyboard.
- main(){ --- This line lets the compiler know (see compiler above) that this is the beginning of the program.
- int A, B, C; --- This line sets up memory (RAM) for the variables that will be needed later while the program runs.
- cout << "Give me your first number:" << endl; --- This line just prints the line "Give me your first number:" to the screen.
- cin >> A; --- This line takes the input from the keyboard and stores it in the memory set up for the variable A that was set up above.
- cout << "Give me your second number:" << endl; -- These next two lines do the same as the two lines above.
- C = A+B; --- These line adds the integers taken from the keyboard above, sums the integers and stores them in the variable C.
- cout << "The answer is:" << C << endl; --- This line prints out the result.
cin >> B;
The following is the program running. As you can see it is just
a text based program with no graphical user interface:
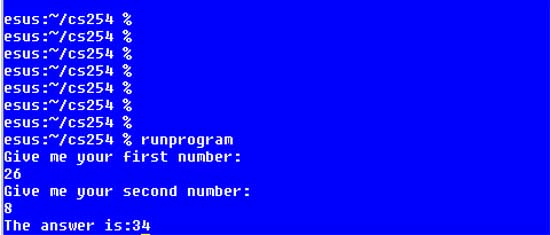
This is a very simple program, it should be noted that a program
such as Word can have millions of lines of code, with teams of
programmers working on all the different facets of the program.
Errors
There are two type of errors that programmers have to deal with when programming- Syntax or Compile time errors - These are errors that happen because the programmer has done something wrong when typing in the source code.
- These errors show up when the source code is put through the compiler application.
- In the above code you can see every instruction ends with a semi-colon. This tells the compiler this instructions is done and your ready to start the next instruction. If the programmer forgets the semi-colon the compiler will get confused and generate an error without generating the machine language.
- These errors are easily found.
- Run-time errors - These errors make the program fail while the program is running.
- These errors are usually much harder to find and sometimes are not discovered until the program is commercially sold. Some of you might have even discovered a run-time error when you get the pop-up screen "this program has completed an illegal operation".
- An example of an error that would only be discovered if the right combination of actions happen could be shown with the program above.
- If the program above would divide variables A and B instead of add them then an run-time error could easily be seen.
- C = A / B;
- If a user inputs a 5 for the variable 'A' and a zero for the variable 'B' then the equation would look like this:
- C = 5 / 0;
- This would be a divide by zero which is illegal in math. An illegal operation such as divide by zero would cause a program to crash.
Control Structures
Control Structures - tell the programs which
action to take.
- An example of a control structure - What if
- If you are playing a game and you make your character turn right there is probably a control structure as above that says if the players turns left then do something else if they go some other way do the second thing. Since you turned right the second thing would be executed.
- There are many different kinds of control structures, and different programming languages haven't different versions of many different types of programming languages.
- Every programming language has to have two control structures (most have several versions of each).
- Iteration loop - that program will keep doing things over and over until a certain condition is met.
- The If statement above, if a certain condition exists do something, if it doesn't exist do something else.
-
if ( A > B) then
do this part of code
else
do this part of code
Programming languages
Hundreds of programming languages exist, but only a handful are used for most commercial applications that exists today.- Basic - One of the first programming languages used on personal PC's, used by Bill Gates. It was originally a programming language teaching tool, but it has since been developed to use in many other cases such as creating business applications. A small version of Basic is used quite often in forms and interactivity on the Web
- Cobol - developed in early 1960's, but still used today mostly in business applications.
- C - developed in early 1970's. Many programs from business apps to operating systems are written in C and it's newer extension C++.
- C++ - produced about ten years of the original C, C++ is an extension of the C programming language. This and Java are the two programming languages that we teach here at MSU. C++ is an object oriented language which is defined below and will be on the test.
- Java - is another object oriented language, the key to Java is it is platform independent. It is one of the most used programming languages today.
Object Oriented approach to programming
It's the newest philosophy of programming. The philosophy is that a programmer
can create a piece of code (called a module) that completes a task. If there
is another program that needs that same task you can just plug that module in
to the new program.